News
Taiwan rattled by 5.6 magnitude quake, no reports of damage
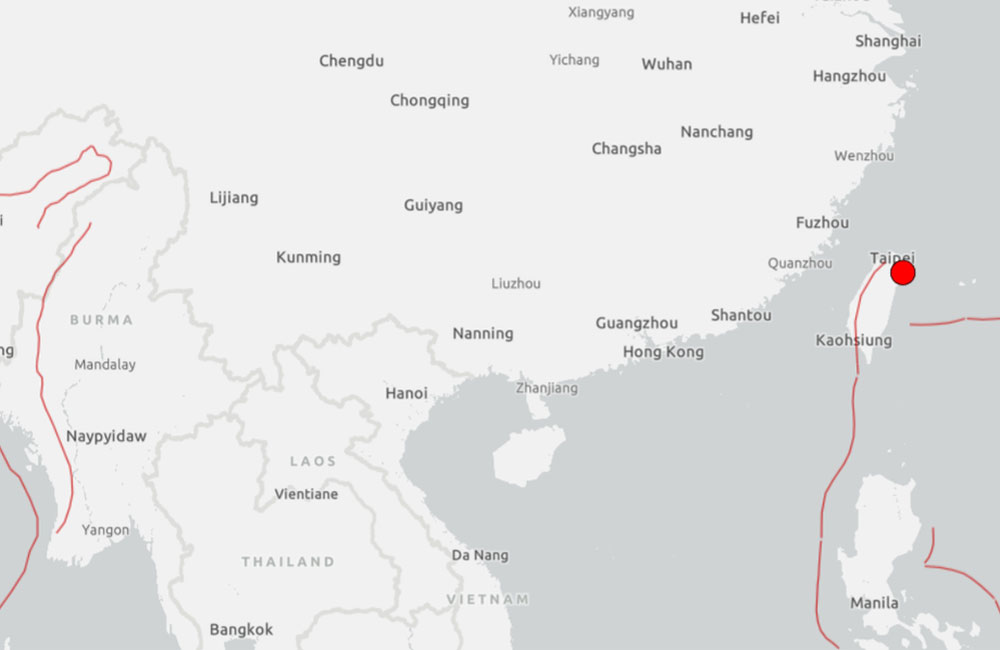
A 5.6 magnitude earthquake struck just off the coast of Taiwan’s northeastern county of Yilan on Tuesday, the island’s weather administration said, with no reports of damage.
The quake briefly shook buildings in the capital, Taipei. The quake had a depth of 66.8 km (41.5 miles), the weather administration said.
The fire department said the quake’s epicentre was 16.9 km (10.5 miles) from the county government seat and in coastal waters.
Taiwan lies near the junction of two tectonic plates and is prone to earthquakes.
More than 100 people were killed in a quake in southern Taiwan in 2016, while a 7.3 magnitude quake killed more than 2,000 people in 1999.
Source:adaderana.lk

Oxford, Cambridge Unions cancel Namal Rajapaksa speaking events
The Oxford Union has cancelled a planned speaking event featuring Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna (SLPP) MP Namal Rajapaksa, following backlash from Tamil student groups and campaigners.
The Cambridge Union had previously cancelled his scheduled appearance, citing security concerns linked to planned protests.
According to UK student newspaper Cherwell, Oxford Union President Katherine Yang said the decision was taken after concerns were raised about students’ ability to participate freely.
“A core part of the Union’s purpose is enabling direct, open questioning from students. In this case, a significant number of the students most closely connected to the subject matter communicated that they did not feel safe asking questions openly,” Yang was quoted as saying.
She added that while alternative formats were considered, the inability of those most affected to participate directly undermined the substance of the forum.
“An event where key stakeholders cannot engage on equal footing does not produce the kind of robust debate the Union is intended to facilitate,” she said.
Rajapaksa is currently on a visit to the United Kingdom and earlier paid homage at the London Buddhist Vihara, which is marking its 100th anniversary this year.
Diaspora advocacy group Tamil Solidarity had called on both unions to cancel Rajapaksa’s scheduled speaking engagements, arguing that providing him a platform amounted to political rehabilitation. The organisation also warned of protests if the events proceeded.
Tamil Solidarity, established in 2009, campaigns on issues related to alleged war crimes, accountability and the rights of Tamil-speaking people.
(Source:Newswire)

Customs Officers Begin Trade Union Action Over Long-Pending Promotions
The Customs Trade Union Alliance has initiated trade union action beginning today (24), highlighting several outstanding concerns that remain unaddressed, including long-delayed promotions.
Union representatives stated that these matters have been repeatedly brought to the attention of relevant authorities over the past six years, but no satisfactory solutions have been reached.
As part of the initial phase of industrial action, Customs officers across all offices islandwide will report to duty wearing black armbands as a mark of protest.
Meanwhile, a special meeting involving the Ministry of Finance Sri Lanka, the Public Service Commission Sri Lanka, and other stakeholders has been scheduled for February 26, 2026, to discuss the issues raised by the union.
Following the outcome of that discussion, representatives of the Customs Trade Union Alliance are expected to convene on February 27 to determine their next steps regarding further industrial action.

EU says it will accept no increase in US tariffs after Supreme Court ruling: ‘a deal is a deal’
The European Commission demanded on Sunday that the United States stick to the terms of an EU-U.S. trade deal reached last year, after the U.S. Supreme Court struck down Donald Trump’s global tariffs and he responded with new levies across the board.
The Commission, which negotiates trade policy on behalf of the 27 EU member states, said Washington must provide “full clarity” on the steps it intends to take following the court ruling.
After the court struck down Trump’s global tariffs on Friday, the U.S. president announced temporary, across-the-board tariffs of 10%, which he then hiked to 15% a day later.
“The current situation is not conducive to delivering ‘fair, balanced, and mutually beneficial’ transatlantic trade and investment, as agreed to by both sides” in the joint statement setting out the terms of last year’s trade agreement, the Commission said. “A deal is a deal.”
The comments were far more strongly worded than the Commission’s initial response on Friday, which had said only that it was studying the outcome of the Supreme Court decision and keeping in contact with the U.S. administration.
Last year’s trade deal set a 15% U.S. tariff rate for most EU goods, apart from those covered by other sectoral tariffs such as on steel. It also allowed zero tariffs on some products such as aircraft and spare parts.
The EU agreed to remove import duties on many U.S. goods and withdrew a threat to retaliate with higher levies.
“In particular, EU products must continue to benefit from the most competitive treatment, with no increases in tariffs beyond the clear and all-inclusive ceiling previously agreed,” the EU executive said, adding that unpredictable tariffs were disruptive and undermined confidence across global markets.
It said that EU Trade Commissioner Maros Sefcovic had discussed the issue with U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer and Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick on Saturday.
Source:Adaderana.lk

Suspect Arrested in Batapola with Stolen Motorcycle Using Fake Number Plates
Officers from the Sri Lanka Police have taken a suspect into custody in the Batapola area of Galle after uncovering a stolen motorcycle concealed inside a residence.
The operation was conducted by the Galle Divisional Crime Investigation Bureau following intelligence received about the hidden vehicle. During the raid, police recovered a motorcycle that had been fitted with falsified number plates.
The suspect, a 30-year-old resident of Ethkandura, was arrested at the location.
Initial inquiries revealed that the motorcycle had been reported stolen in 2024 within the Karandeniya Police Division. Further investigations also indicated that the suspect had links with individuals believed to be involved in organized criminal activities.
Authorities are continuing their investigation to determine whether the stolen motorcycle had been used in any criminal offences.

NBRO Lifts Red Landslide Alerts; Amber and Yellow Warnings Still Active in Several Districts
The National Building Research Organisation has removed the previously issued Red-level landslide warnings for several districts after observing a decline in rainfall over the past 24 hours.
NBRO scientist Suminda Ratnayake explained that the decision was made after evaluating recent weather patterns and updated forecasts, which indicated an improvement in conditions.
Despite the removal of the highest-level warning, Level 2 (Amber) alerts, urging residents to remain alert, are still in place for several Divisional Secretariat divisions. These include Yatinuwara, Doluwa, Ududumbara, Ganga Ihala Korale, Pathadumbara, and Medadumbara in Kandy District; Yatiyanthota, Kegalle, Dehiowita, Aranayaka, and Mawanella in Kegalle District; Rattota, Ambagamuwa Korale, Laggala Pallegama, Wilgamuwa, and Ukuwela in Matale District; Walapane, Ambagamuwa, and Nildandahena in Nuwara Eliya District; Kalawana, Ayagama, Kiriella, and Ratnapura in Ratnapura District; Badalkumbura in Monaragala District; Haldummulla in Badulla District; and Niyagama in Galle District.
In addition, Level 1 (Yellow) warnings, advising vigilance, have been issued for 23 Divisional Secretariat divisions across the districts of Badulla, Galle, Hambantota, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala, Matale, Monaragala, Nuwara Eliya, and Ratnapura.
Dr. Ratnayake cautioned that although rainfall has reduced, the ground in previously affected areas remains heavily saturated. He warned that even light showers could trigger landslides, rockfalls, or earth slips. Residents and travelers in vulnerable areas have been urged to stay alert, monitor official advisories, and take precautionary measures to ensure their safety.

Storm paralyzes travel, forcing more than 8,000 US flight disruptions
U.S. airlines are set to add flights on Tuesday, even as they wrestle with thousands of scrubbed flights the day after a powerful Northeast winter storm forced more than 8,000 cancellations and delays.
The storm blanketed parts of the U.S. Northeast, closing roads and cancelling schools.
With cancellations frustrating travelers on Monday evening, U.S. carriers including United Airlines UAL.Osaid they had early plans to ramp up operations on Tuesday, but cautioned that conditions remain challenging.
On Tuesday, 7% of U.S. flights are expected to be cancelled, down from just over 19% on Monday, according to data from analytics firm Cirium as of late afternoon. A typical day in the U.S. domestic market has 1% cancellations.
Southwest Airlines LUV.Nsaid its plan “is on track to start ramping up operations tomorrow, if conditions permit us to safely do so.”
The Dallas-based low-cost carrier canceled about 7% of flights on Monday. That was less than its rivals due to the carrier’s limited Northeast exposure.
American Airlines AAL.O said it had been able to resume operations at Washington Reagan National and Philadelphia.
Delta DAL.N and American both said they expect to resume operations at New York’s LaGuardia and JFK airports and Boston late on Tuesday morning. Delta also expects to resume Newark flights on Tuesday.
JetBlue JBLU.O was especially hard hit, canceling about 80% of flights due to the storm on Monday, according to data from FlightAware. The airline said in total it has cancelled 1,600 flights through Wednesday.
U.S. passenger railroad Amtrak canceled dozens of trains between New York and Boston and on other routes in the Northeast. Several states ordered motorists to remain off roads for non-essential travel for extended periods due to the significant snowfall.
American, Delta and United all canceled about 20% of flights on Monday.
The blizzard dropped more than 2-1/2 feet of snow (76.2 cm) across parts of the U.S. Northeast.
Source:adaderana.lk

New York, other US states under state of emergency as snow falls amid blizzard warning
New York, New Jersey, Connecticut and Massachusetts governors issued state of emergency orders and a halt to non-essential travel as a major storm was expected to bring up to 24 inches of snow and strong winds to the region.
• Around 15,247 flights were delayed by early afternoon on Sunday, and 3,509 were cancelled. The largest number of cancellations were at JFK, La Guardia and Newark airports.
• New York City Mayor Zohran Mamdani ordered the closure of city streets to non-essential vehicular traffic, including bicycles and scooters, from 9 p.m. Sunday to 12 p.m. Monday and closure of all school buildings.
• Similar restrictions were adopted by Connecticut, as Governor Ned Lamont banned commercial vehicles on highways in the state from 5 p.m. on Sunday.
• Massachusetts Governor Maura Healey has declared a state of emergency and activated up to 200 National Guard members to help. The state also restricted non-essential travel from Sunday evening.
• New York Governor Kathy Hochul activated 100 National Guard members to deploy in Long Island, New York City and the Lower Hudson Valley.
Source:adaderana.lk
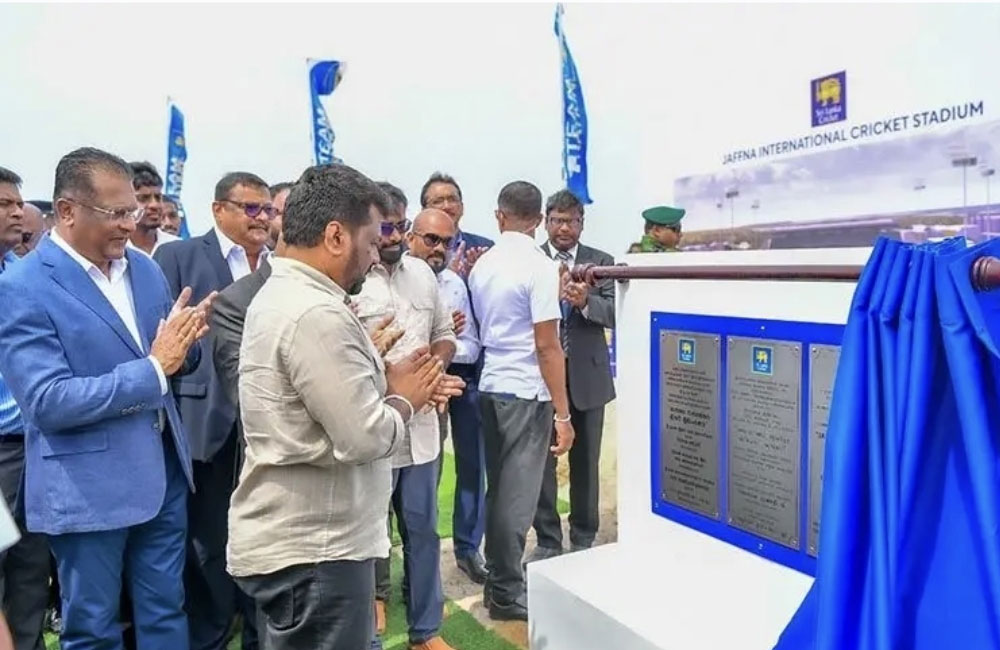

Construction of Jaffna International Cricket Stadium Suspended Over Missing Environmental Clearance
Construction activities on the planned international cricket stadium in Mandaitivu, Jaffna, have been temporarily stopped after it was found that the required Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) had not been approved.
According to Central Environmental Authority Sri Lanka Chairman Tilak Hewawasam, instructions have been issued to suspend all ongoing work until the necessary environmental evaluation is completed and official approval is obtained. The decision was taken after authorities confirmed that environmental clearance had not been secured before construction began.
The project was initiated last year, with the foundation stone laid by President Anura Kumara Dissanayake as part of plans to establish the first international cricket stadium in Northern Sri Lanka.
Mandaitivu Island, where the stadium is being built, is recognized as an environmentally sensitive region. The area includes important coastal ecosystems such as mangroves, wetlands, salt marshes, mudflats, and seagrass habitats. The project site is located close to the Mandaitivu Mangrove Reserved Forest and falls within a zone classified as highly sensitive under regional environmental guidelines.
Environmental organizations have previously warned that large-scale infrastructure projects in the area could harm fragile ecosystems and threaten biodiversity if proper safeguards are not enforced.
The proposed stadium is part of a broader initiative to develop Mandaitivu Island into a sports hub with international-level facilities. The long-term plan includes additional developments such as a swimming complex, indoor sports facilities, hotels, residential apartments, retail outlets, and entertainment venues.
The stadium construction is planned in four stages, with the initial phase focused on preparing the ground and pavilion to accommodate domestic cricket matches. Work is expected to resume once all environmental requirements are fulfilled and approval is granted by relevant authorities.
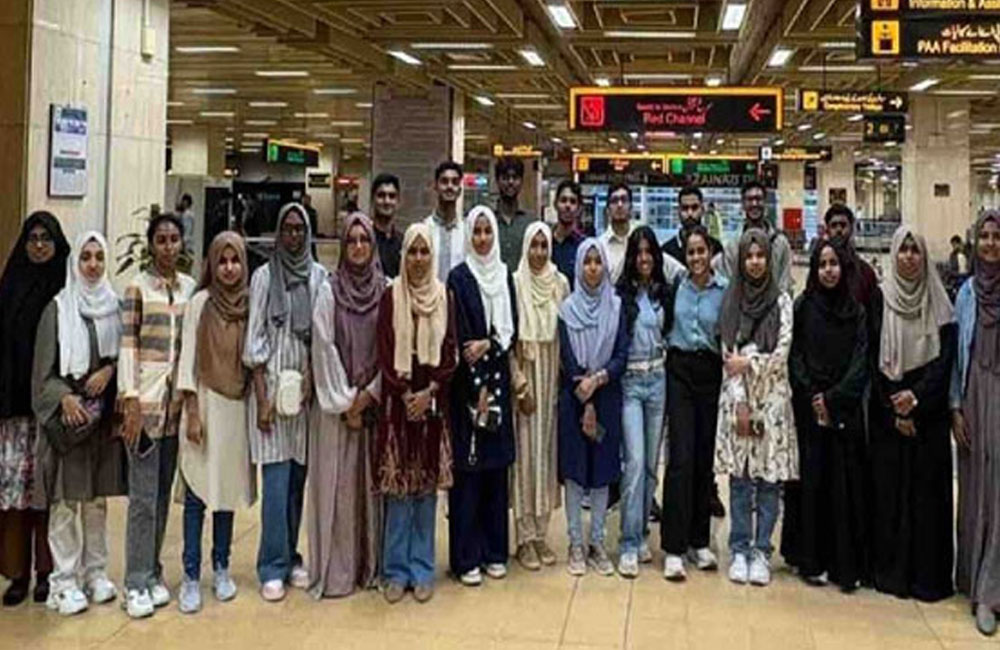

25 Sri Lankan students land in Pakistan for medical studies
Twenty-five Sri Lankan students have landed in Pakistan to study MBBS in top medical universities through the Allama Iqbal Scholarships for Sri Lankan Students.
The students were welcomed upon their arrival at Jinnah International Airport, Karachi.
These fully-funded scholarships are a part of the larger Pak-Sri Lanka Higher Education Cooperation Programme, which is managed by the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan.
Through this initiative, the students will be able to carry out their medical studies at top universities, including Dow University of Health Sciences (DUHS) Karachi and Liaquat University of Medical & Health Sciences (LUMHS), Karachi.
Both of these universities are properly recognized by the Sri Lankan Medical Council (SLMC), which will make the degrees internationally recognized.
Apart from the students who have just arrived, there are over 430 Sri Lankan students who are currently enrolled in Pakistani universities through this scholarship program in a variety of disciplines, including Medicine, Engineering, Business Studies, Natural Sciences, and Social Sciences.
All of these students have been selected through a competitive process, as per the eligibility criteria for admission to Pakistani higher education institutions. Through the same scholarship program, one hundred more Sri Lankan students are set to arrive in Pakistan.
Source:adaderana.lk

Afternoon Showers Forecast; Rough Seas Expected Due to Low-Pressure System
The Department of Meteorology Sri Lanka has predicted mainly fair weather across much of the island today, with rain expected in selected areas after 2.00 p.m.
Showers or thundershowers are likely to develop in parts of the Southern Province, as well as in the districts of Ratnapura, Monaragala, and Kalutara during the afternoon hours. The public has been advised to take precautions against localized strong winds and lightning that may accompany thundershowers.
Meanwhile, a low-pressure system situated over the Bay of Bengal, northeast of Sri Lanka, is gradually moving in a northeasterly direction and is expected to weaken further. However, its influence could still result in heavy showers or thundershowers and strong winds reaching speeds of 50–60 kmph in certain areas.
As a result, sea conditions may turn rough at times. Naval personnel and fishing communities have been urged to remain alert.
Rain or thundershowers may also occur in sea areas extending from Galle to Pottuvil via Hambantota during the evening or night. Winds around the island’s coastal waters are expected to be north-westerly, with speeds ranging between 20 and 40 kmph.
Overall, sea conditions will be moderate, but temporarily strong gusts and very rough seas can occur during thundershowers, according to the department.
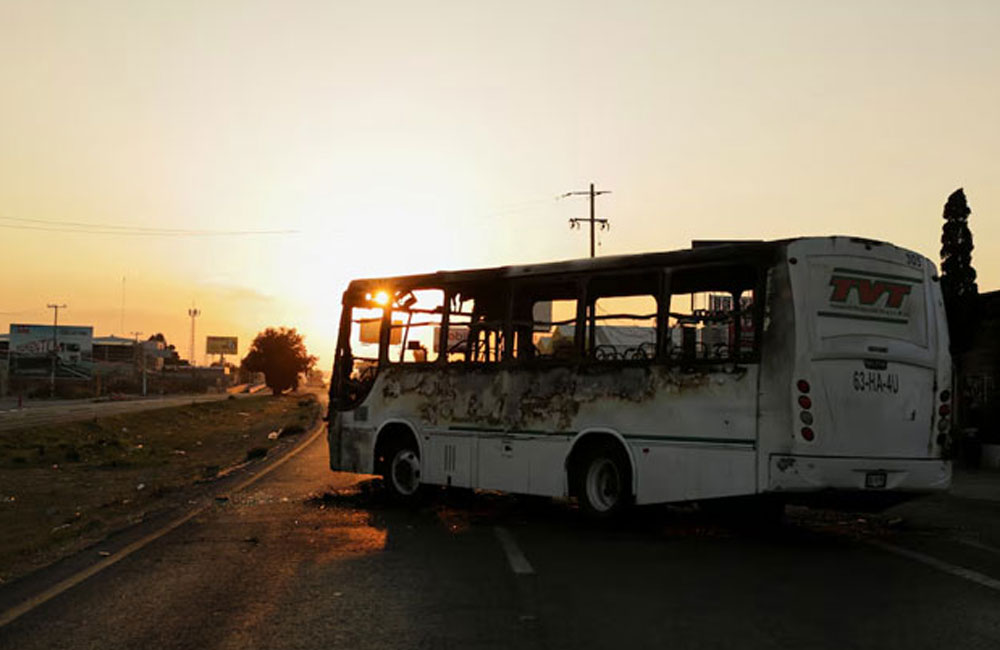

Mexican drug lord killing sparks revenge attacks; cars and businesses set ablaze, highways blocked
Within hours of the killing of Mexican drug lord Nemesio Oseguera, better known as El Mencho, in a military raid on Sunday, gunmen suspected to be his supporters blocked highways across several states and set cars and businesses ablaze.
In some towns tourists and residents were urged to stay indoors, while truckers were advised to take safe routes or return to their depots until the violence abated.
Several airlines, including Air Canada, United Airlines and Aeromexico, on Sunday cancelled flights to Puerto Vallarta, a beachside resort town where stunned tourists filmed plumes of smoke rising into the sky from fires.
The burst of violence across more than half a dozen states painted a familiar scene for Mexicans who have spent two decades watching successive governments wage war on drug cartels, ravaging broad swaths of the country.
A member of Oseguera’s Jalisco New Generation Cartel told Reuters that the blazes and sporadic gunfire were carried out in revenge for the government’s killing of Oseguera, and warned of further bloodshed as groups move to take control of his cartel.
“The attacks were carried out in revenge for the leader’s death, at first against the government and out of discontent,” the person said, speaking on condition of anonymity.
“But later the internal killings are coming, by the groups moving in to take over.”
In Mexico’s Pacific coast, a five-hour drive from the military operation in the town of Tapalpa that took down the leader of the powerful Jalisco New Generation Cartel, stunned beachgoers on a pier in Puerto Vallarta took out their cell phones to film thick waves of smoke obscuring blue ocean views, showed a video shared with Reuters.
Daniel Drolet, a Canadian who has wintered in Puerto Vallarta for years, said in a phone interview that he was concerned of a new era of violence taking root in the typically placid resort zone.
“I have never seen anything like this before,” he said.
In the state of Jalisco, authorities reported that gunmen had attacked a base for the National Guard military police, and recommended guests remain inside hotels and suspended public transit.
Other scenes of criminal activity and military response were captured in videos shared by government security sources with Reuters: A green military tank made its way through a residential neighborhood in the state of Aguascalientes. Roadblocks paralyzed the highly transited Mexico-Puebla highway. In the state of Colima, cartel members standing in pick-up trucks blocked a road.
A trucking industry group said in a statement it was “profoundly worried” by the highway violence and recommended that truckers keep to safe areas or return to their operating yards until conditions improved.
The state of Guanajuato, a CJNG stronghold, reported 55 incidents across 23 municipalities, with 18 arrests, but said by evening all incidents were under control.
Carlo Gutierrez, who lives in Guadalajara, Jalisco’s capital, said that friends on WhatsApp groups were encouraging people to stay home.
“There is fear and a lot of caution,” he said of the city, one of three main Mexican venues for World Cup soccer matches this summer.
VIOLENCE IN WAKE OF CARTEL ARRESTS, KILLINGS
Authorities have not reported any casualties beyond several cartel members and officials killed during the military operation.
Previous cartel arrests and killings have led to outbreaks of violence - whether by members avenging their fallen leader or rival gangs muscling in on their territory - prompting Mexican authorities to hesitate before launching major campaigns.
In 2019, Ovidio Guzman, a son of Sinaloa Cartel kingpin Joaquin “El Chapo” Guzman, was detained but quickly released, setting off widespread gun battles. His arrest in 2023 set off more violence.
The 2024 arrest of Sinaloa Cartel boss Ismael “El Mayo” Zambada triggered a bloody power struggle in the criminal group that continues unabated more than a year later.
“I’m watching the scenes of violence from Mexico with great sadness and concern,” said U.S. Deputy Secretary of State Christopher Landau, who previously served as ambassador to Mexico, in a post on social media.
“It’s not surprising that the bad guys are responding with terror. But we must never lose our nerve.”
Mexico’s President Claudia Sheinbaum in a social media post acknowledged the violence, but struck a tone of calm.
“In most of the national territory activities are happening with absolute normalcy,” she said.
Source:adaderana.lk
Page 6 of 681